FITS images header and coordinates
APLpy
To make beautiful plots with Python: https://aplpy.github.io
FITS and WCS
Intro
FITS header < FITS format from IAU FITS Working Group!
Official reference documentation: http://fits.gsfc.nasa.gov/fits_standard.html
The FITS header
It's the astronomical standard metadata! Specifies all useful information associate with your data (obtaining conditions, reducing history, etc).
The header is a table with three possible fields:
Keyword; Value; Comment
Keywords must start with a text character.
Value can be of multiple types (interger, float, string).
[Optional] Comment text.
FITS Header example
SIMPLE = T / Standard FITS format
BITPIX = 16 / Number of bits for each pixel
NAXIS = 2 / Number of axes in frame
NAXIS1 = 2148 / Number of pixels per row
NAXIS2 = 4100 / Number of rows
BUNIT = 'ADU ' / Unit of original pixel value
CTYPE1 = 'pixel ' / Pixel coordinate system
CTYPE2 = 'pixel ' / Pixel coordinate system
CRPIX1 = 1 / Reference pixel in axis1
CRVAL1 = 1 / Physical value of the reference pixel
CDELT1 = 1 / Size projected into a detector pixel in axis1
CRPIX2 = 1 / Reference pixel in axis2
CRVAL2 = 1 / Physical value of the reference pixel
CDELT2 = 1 / Size projected into a detector pixel in axis2
...
OBJECT = ' BD+28.4211 ' / Target Description
DATA-TYP= 'OBJECT ' / Characteristics of this data
RA = '21:51:12.055' / RA of the tracked pos. on the slit guide pos.
DEC = '+28:51:38.72' / Dec of the tracked pos. on the slit guide pos.
...Coordinates and projections
FITS conventions has been defined to specify the physical, or world, coordinates to be attached to each pixel of an N-dimensional image (http://fits.gsfc.nasa.gov/fits_wcs.html)
Paper I (units and world coordinates).
Paper II: celestianl coordinates and projection [!] schemes.
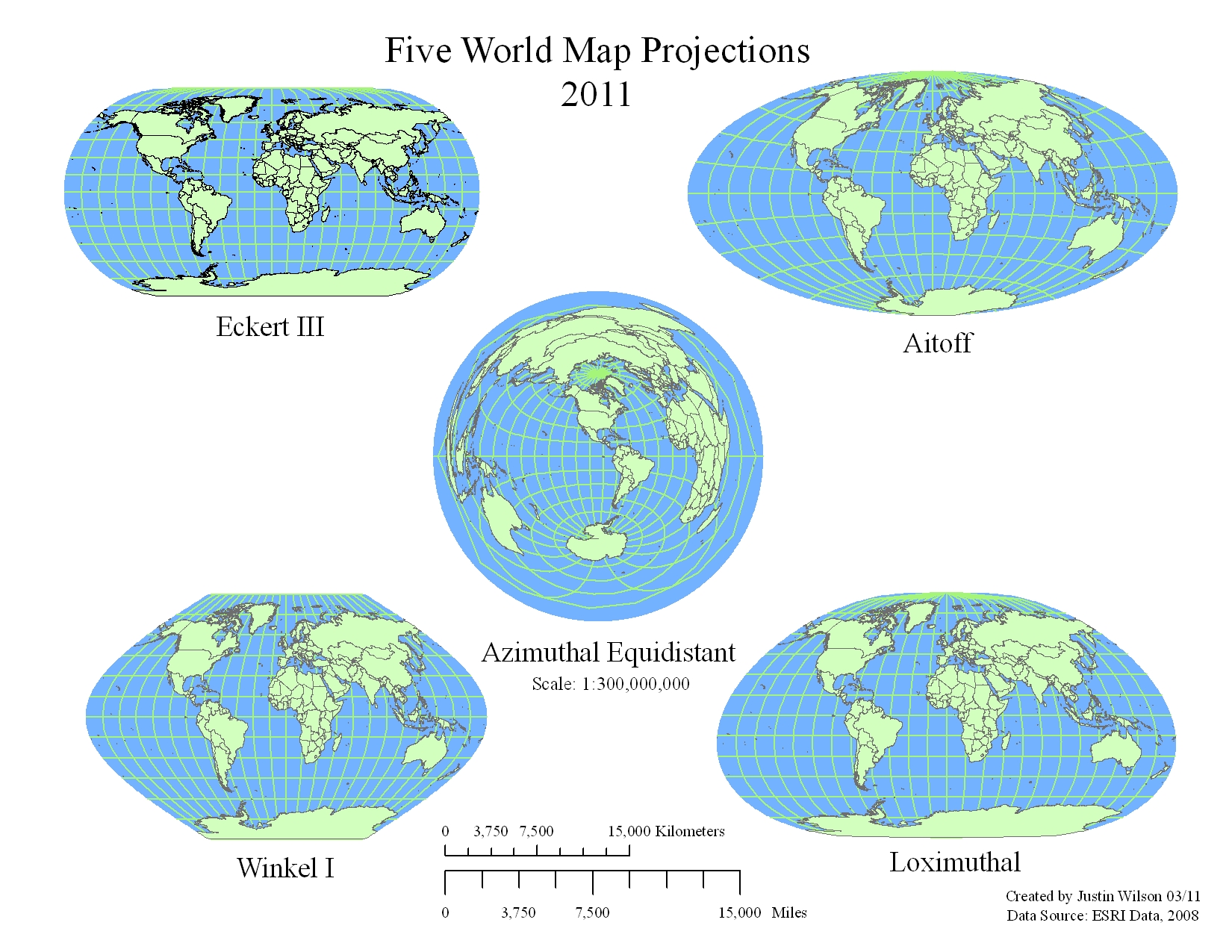
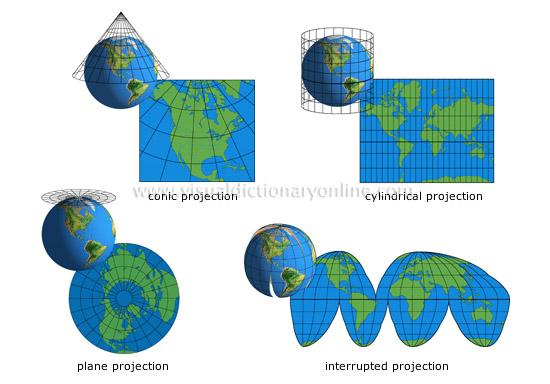
FITS Header and the WCS
World Coordinate System (WCS) keywords in the header of a FITS or IRAF image file define the relationship between pixel coordinates in the image and sky coordinates.
There are 25 projections of the proposed FITS WCS standard (http://tdc-www.harvard.edu/wcstools/wcstools.wcs.html):
AZP: Zenithal (Azimuthal) Perspective
SZP: Slant Zenithal Perspective
TAN: Gnomonic = Tangent Plane
SIN: Orthographic/synthesis
STG: Stereographic
ARC: Zenithal/azimuthal equidistant
ZPN: Zenithal/azimuthal PolyNomial
ZEA: Zenithal/azimuthal Equal Area
AIR: Airy
CYP: CYlindrical Perspective
CAR: Cartesian
MER: Mercator
CEA: Cylindrical Equal Area
COP: COnic Perspective
COD: COnic equiDistant
COE: COnic Equal area
COO: COnic Orthomorphic
BON: Bonne
PCO: Polyconic
SFL: Sanson-Flamsteed
PAR: Parabolic
AIT: Hammer-Aitoff equal area all-sky
MOL: Mollweide
CSC: COBE quadrilateralized Spherical Cube
QSC: Quadrilateralized Spherical Cube
TSC: Tangential Spherical Cube
NCP: North celestial pole (special case of SIN)
GLS: GLobal Sinusoidal (Similar to SFL)
WCS Keywords basics
CTYPE1 and CTYPE2 indicate the coordinate type and projection.
CTYEP1 = xxxxyyyy / 'Comment' CTYEP2 = xxxxyyyy / 'Comment'
The first four characters are RA-- and DEC-, GLON and GLAT, or ELON and ELAT, for equatorial, galactic, and ecliptic coordinates, respectively.
The second four characters contain a four-character code for the projection.
CRPIX1 and CRPIX2 are the pixel coordinates of the reference point to which the projection and the rotation refer.
CRVAL1 and CRVAL2 give the center coordinate as right ascension and declination or longitude and latitude in decimal degrees.
WCS rotation
Many astronomical instruments provide image files in which the 'x' and 'y' coordinate axes are not orientated with equatorial north corresponding to 'up' (and east == 'left'). According to WCS, there are three options for the scale and rotation:
Historically, CDELT1 and CDELT2 have been used to indicate the plate scale in degrees per pixel and CROTA2 has been used to indicate the rotation of the horizontal and vertical axes in degrees. Usually the axes rotate together and CROTA2 is used to indicate that angle in degrees.
The FITS WCS standard uses a rotation matrix, CD1_1, CD1_2, CD2_1, and CD2_2 to indicate both rotation and scale, allowing a more intuitive computation if the axes are skewed. This model has been used by HST and IRAF for several years.
CD1_1 = CDELT1 * cos (CROTA2)
CD1_2 = -CDELT2 * sin (CROTA2)
CD2_1 = CDELT1 * sin (CROTA2)
CD2_2 = CDELT2 * cos (CROTA2)
The 1996 proposed FITS WCS standard used PC001001, PC001002, PC002001, and PC002002 to represent the rotation matrix but retained CDELT1 and CDELT2 for the scale. It is also read by this software, but should not be used for new WCS's.
ALMA OST requeriments
OST = Observation Support Tool, http://almaost.jb.man.ac.uk
[BUNIT:] The physical units of the FITS image array values.
CDELTn*: Coordinate increment along axis n.
[CROTAn]: Coordinate system rotation angle.
[CDn_n]: Usually a matrix of four values which describe the mapping of the Coordinate system within the FITS image, i.e both increment and rotation. CDn_n matrix values and CDELTn and CROTAn are degenerate.
CTYPEn: Name of the CDELTn coordinate axis.
NAXIS: Number of axes.
NAXISn: Size of the axis n.
CRVAL3: good to save wavelength info.
From an image to ALMA!
Attention! ALMA OST do not rotate images for now. Instead it assumes that an uploaded image does have equatorial north corresponding to 'up' (http://almaost.jb.man.ac.uk/help/#Rotation).
Suggestion - use of PyHdust (http://github.com/danmoser/pyhdust).
One example: ramp image with 2 AU in size at 10 parsecs, rotated at 45 degree (by definition, to east) at 21 cm.
import numpy as np
import pyhdust.phc as phc
import pyhdust.interftools as intt
img = np.arange(900).reshape((30,30))
intt.img2fits(img, 21., [2*phc.au.cgs/phc.Rsun.cgs], 10, orient=45., \
coordsinf=['21:51:12.055', '-28:51:38.72'], ulbd='cm', deg=True)
intt.img2fits(img, 21., [2*phc.au.cgs/phc.Rsun.cgs], 10, rot=45., \
coordsinf=['21:51:12.055', '-28:51:38.72'], ulbd='cm', deg=True, \
outname='model_rotated')Output - Coordinate rotation:
Output - Image rotation: